| | Date | Content in Textbook |
|
| | Wed, 1/22 |
- 1.1 Definitions of Statistics, Probability , and Key Terms
- a) Distinguish populations and samples
- b) Distinguish parameters and statistics
- 1.2 Data, Sampling, and Variation in Data and Sampling
- a) Classify data into categories of categorical, quantitative, discrete, continuous.
- b) Distinguish different types of sampling 1
|
|
| | Fri, 1/24 | Letter, Quiz 1 |
|
| | Mon, 1/27 |
- 1.3 Frequency, Frequency Tables, and Levels of Measurement
- a) Differentiate data by levels of measurement
- b) Construct frequency, relative frequency tables, and cumulative relative frequency tables Lab 1
- 1.4 Experimental Design and Ethics
- a) Distinguish explanatory, response, and treatments variables
- b) Discuss lurking variables, placebo, and control groups
|
|
| | Wed, 1/29 |
- 2.1 Stem-and-Leaf Graphs (Stemplots), Line Graphs, and Bar Graphs
- 2.2 Histograms, Frequency Polygons, and Time Series Graphs
- a) Construct by hand a Stem & Leaf display
- b) Use software to create charts for categorical data (Lab 1)
- c) Use software to create data displays for quantitative data
- 2.3 Measures of Location of the Data
- a) Use software to calculate and interpret measures relative standing
- b) Use IQR to identify outliers
- c) Apply algorithms for percentiles
- 2.4 Box Plots
- a) Create and interpret boxplots (manually and with software)
|
|
| | Fri, 1/31 |
TEST 1: Chapters 1, 2.1 - 2.4 (10%) |
|
| | Mon, 2/3 |
- 2.5 Measures of the Center of the Data
- a) Distinguish notations for population and sample statistics
- b) Discuss Law of Large Numbers
- 2.6 Skewness and the Mean, Median, and Mode
- a) Discuss symmetry and skewness in data
- 2.7 Measures of the Spread of the Data
- a) Use software to calculate and interpret measures of dispersion (Lab 2)
- b) Calculate z-scores for data
- c) Apply the Empirical Rule and Chebyshev’s Inequality to data 3
|
|
| | Wed, 2/5 |
- 12. 1 Linear Equations
- 12.2 Scatterplots
- 12.3 The Regression Equation
- a) Briefly review linear equations
- b) Construct scatter plots
- c) Discuss the meaning of the correlation coefficient
- d) Discuss the meaning of the coefficient of determination
- e) Use software to calculate the regression statistics (Lab 3)
- f) Interpret the meaning of the regression slope and intercept in the context of applied problems
- g) Assess the suitability of a linear relationship for bivariate data using regression analysis.
Use regression equation for interpolation if appropriate. |
|
| | Fri, 2/7 | Quiz 2 /Lab 2 |
|
| | Mon, 2/10 | open |
|
| | Wed, 2/12 | open |
|
| | Fri, 2/14 |
TEST 2: More Chapter 2 & Ch 12 (10%) |
| | Mon, 2/17x | No School |
|
| | Wed, 2/19 | |
|
| | Fri, 2/21 | Quiz 3 / Lab 3 |
|
| | Mon, 2/24 |
- 3.1 Terminology
- a) Discuss experiments, sample spaces and axioms of probability
- b) Define EVENT as a subset of the sample space
- c) Discuss the Law of Large Numbers (Lab 4)
- d) Discuss an OR events as a union of outcomes
- e) Discuss an AND events as the intersection of outcomes
- f) Discuss complement of an event
- g) Define conditional probability
- 3.2 Independent and Mutually Exclusive Events
- a) Define independent events
- b) Discuss sampling with and without replacement
- c) Find probabilities using complements
- d) Determine if events are independent and/or mutually exclusive
|
|
| | Wed, 2/26 |
- 3.3 Two Basic Rules of Probability
- a) Find probabilities using the Multiplication Rule
- b) Find probabilities using the Addition Rule
- 3.4 Contingency Tables
- a) Construct two-way tables for multivariate data
- b) Use contingency tables to find conditional and marginal probabilities
|
|
| | Fri, 2/28 | Quiz 4 / Lab 4 |
|
| | Mon, 3/3 |
- 3.5 Tree and Venn Diagrams
- a) Create Tree Diagrams to represent a sample space and aid to find probabilities
- b) Create Venn Diagrams to represent a sample space and aid to find probabilities
|
|
| | Wed, 3/5 |
- 4.1 Probability Distribution Function for a Discrete Random Variable
- a) Identify the characteristics of a discrete pdf
- 4.2 Mean or Expected Value and Standard Deviation
- a) Calculate and interpret the expected value of a discrete random variable
|
|
| | Fri, 3/7 | no quiz, happy semester break |
|
| | Mon, 3/10x | No School |
|
| | Wed, 3/12x | No School |
|
| | Fri, 3/14x | No School |
|
| | Mon, 3/17 |
- 4.3 Binomial Distribution
- a) Identify the characteristics of binomial experiment
- b) Use the Binomial distribution to solve applied probability problems
- c) Use software to construct a bar chart for probabilities of a Binomial random variable (Lab 5)
|
|
| | Wed, 3/19 | open |
|
| | Fri, 3/21 |
TEST 3: Chapters 3 & 4 (20%) |
|
| | Mon, 3/24 | |
|
| | Wed, 3/26 |
- 5.1 Continuous Probability Functions
- a) Discuss continuous random variables – define and examples
- b) Properties of continuous probability distributions
- c) Setting up a Uniformly distributed random variable
- 5.2 The Uniform Distribution
- a) Applications involving the Uniform Distribution including percentiles and conditional probabilities
- b) Mean & standard deviation of the Uniform Distribution
|
|
| | Fri, 3/28 | Quiz 5 / Lab 5 |
|
| | Mon, 3/31 |
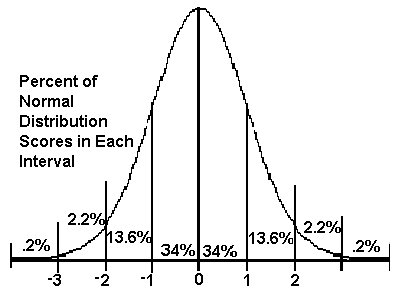
- 6.1 The Standard Normal Distribution
- a) Characteristics of the standard and non-standard normal distribution
- b) Define and interpret z-scores
- c) Apply Empirical Rule
- 6.2 Using the Normal Distribution
- a) Sketch, shade and calculate probabilities
- b) Find percentiles
- c) Solve applied problems
|
|
| | Wed, 4/2 |
- 6.4 Normal Distribution (Pinkie Length)
- a) Students collect data and compare with a theoretical distribution
- b) Include normal probability plots, box plot, histogram (Lab 6)
|
|
| | Fri, 4/4 | Quiz 6 / Lab 6 |
|
| | Mon, 4/7 |
- 7.1 The Central Limit Theorem for Sample Means
- a) Discuss Central Limit Theorem (Lab 7)
- b) Solve applied problems using the Central Limit Theorem
|
|
| | Wed, 4/9 | open |
|
| | Fri, 4/11 |
TEST 4: Chapters 5 – 7 (20%) |
|
| | Mon, 4/14 | |
|
| | Wed, 4/16 |
- 8.1 A Single Population Mean using the Normal Distribution
- a) Define point estimate, margin of error, confidence interval estimate for the mean assuming σ is known, standard error.
- b) Discuss the meaning of a confidence interval estimate (p 449 of text)
- c) Interpret a CI estimate
- d) Discuss width of CI and confidence level
- e) Calculation of sample size needed for particular error tolerance
|
|
| | Fri, 4/18x | |
|
| | Mon, 4/21 |
- 8.4 Confidence Interval (Home Costs)
- a) Students collect data (n=35) and construct 90% CI estimate for mean home cost in Edison NJ
- b) Use s as approximation for σ when constructing CI estimate for mean home cost
|
|
| | Wed, 4/23 |
- 9.1 Null and Alternative Hypotheses
- a) Define null and alternative hypotheses for mean and proportion
- 9.2 Outcomes and the Type I and Type II Errors
- a) Define Type I and Type II error and their meaning in the context of applied problems
|
|
| | Fri, 4/25 | Quiz 7 / Lab 7 |
|
| | Mon, 4/28 |
- 9.4 Rare Events, the Sample, Decision and Conclusion
- a) Define p-value
- b) Discuss the relationship between p-value and hypothesis testing
- c) Identify p-value for HT in a normal curve sketch.
- d) Decision and conclusion for HT
- 9.5 Additional information and Full Hypothesis Test (HT) Examples
- a) Level of significance
- b) Identify random variables relevant to applied problem
- c) Hypothesis test examples for mean using z distribution
- d) Set level of significance, calculate p-values, make a decision, and formulate a conclusion for a HT
|
|
| | Wed, 4/30 | open |
|
| | Fri, 5/2 |
TEST 5: Chapters 8 – 9 (20%) |
|
| | Mon, 5/5 |
Qz/Labs: (10%), Review of Grades, Answer Students' Exam Questions |
|
| | Wed, 5/7 |
Final Exam (10%) |
|