| Basic Vocabulary |
-
- experiment -- an action that is performed
- event -- a result of an experiment or action, an outcome
- outcome -- a result of an experiment or action, an event
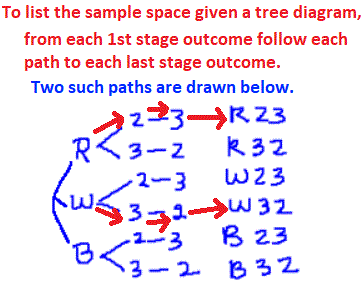
- sample space -- the set of all possible outcomes/results/events of an experiment
|
- independent event - uninfluenced, stand alone, the result of one stage or trial has no effect on another stage or trial.
- ex. Raw sample data - the number of heads when 3 coins are flipped.
- The result of each flip, or trial, is not influenced by the other flips.
- dependent event - having an influence on other stages or trials, the result of one stage of the collection of raw data,
- has an effect on another stage.
- ex. Raw sample data - the names of a president and vice president of a club with 4 members.
- One officer must be picked at a time or you would not know which officer was which.
- For instance: There are 4 choices for president, but only 3 choices for vp.
- The result of the first stage influences the second stage.
|

|
- with replacement - restore the original conditions after each trial. A after a trial or stage, the setting is restored to the original setting before beginning the next trial or stage.
- ex. Raw sample data - draw a card from a deck, replace the card in the deck, draw a card from the deck. The 2 draws are independent. The replacement made each draw have the same outcomes.
- without replacement - do not restore the original conditions after each trial, use the new conditions.
- ex. Raw sample data - draw a card from a deck, draw a 2nd card from the deck.
|
- Probability
- probability of an event -- P(event), or p(event)
- ex. p(A), the probability of event A
- ex. p(head), the probability of obtaining a head
- ex. p(x=3), the probability the variable is 3 or the probability of the number 3 occuring, or the probability of obtaining a 3.
- probability of an event, P(event) = f/n,
| | (frequency of the event) |
| P(event) = |
|
| | (number of events in the sample space) |
-
- Facts
- The lowest possible probability an outcome might have is 0.
- If P(event)=0, the event can not happen.
- The highest possible probability an outcome might have is 1.
- If P(event)=1, the even does happen.
- Probabilities range between 0 and 1, inclusive.
- 0 < P(event) < 1.
- The sum of all the probabilities for an experiment is 1.
- ex. Experiment: flip a fair coin.
- P(head) + P(tail) = 1
- ex. Experiment: flip a weighted coin.
- P(head) + P(tail) = 1
| - ex. Experiment: pick a day of the week.
- p(Sunday) + p(Monday) + ... + p(Saturday) = 7/7 = 1
- ex. Experiment: pick a day of the week
- p(January) = 0
|
|
| Probability in Words, & Symbols, & Computation |
| Words | Symbols | Computation |
|
| an event , EVENT | E | |
|
| probability of event | P(EVENT) | P(event) = f/n,
| | (frequency of the event) |
| P(event) = |
|
| | (number of events in the sample space) | |
|
| probability of event A | P(A) | P(A) = f/n,
| | (frequency of the event A) |
| P(A) = |
|
| | (number of events in the sample space) | |
|
| probability of event B | P(B) | P(B) = f/n,
| | (frequency of the event B) |
| P(event) = |
|
| | (number of events in the sample space) | |
|
probability of either event A occurring or event B occurring
or both happening
-- OR as in a union of outcomes
If A and B are mutually exclusive events, then
P(A OR B) = P(A) + P(B), because P(A AND B)= 0 | P(A OR B) | P(A OR B) = P(A) + P(B) - P(A AND B) |
|
probability of both event A and event B occurring
-- AND as in the intersection of outcomes | P(A AND B) | P(A and B) = P(A)P(B)
|
|
| probability of event A happening given that
even B has happened | P(A GIVEN B) or P(A|B) | P(A|B) = P(A AND B)/P(B) |
|
| probability of event B happening given that event A has happened | P(B GIVEN A) or P(B|A) | P(B|A) = P(A AND B)/P(A) |
|
| probability of A times the probability of B | P(A)P(B) | |
|
|