To be BINOMIAL:
- There are n, a specific number, of trials -- n identical actions.
- Each trial is independent -- the result of one trial has no effect on another trial.
- Each trial has only 2 outcomes -- success or failure.
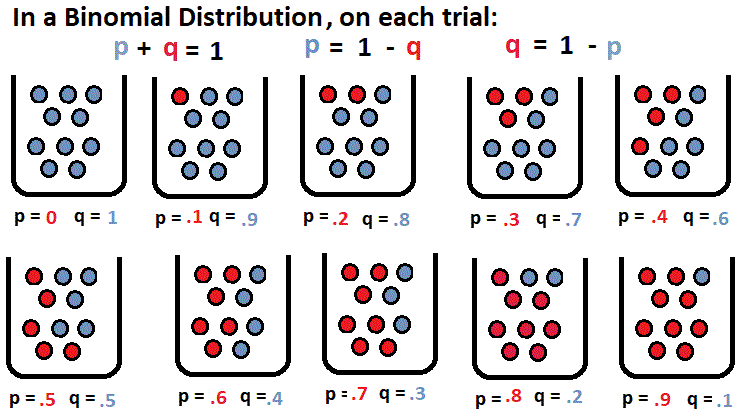
The probabililty of success on a trail is called p.
P(success) = p.
The probabililty of failure on a trail is called q.
P(failure) = q.
This also means that q = 1 - p and p = 1 - q.
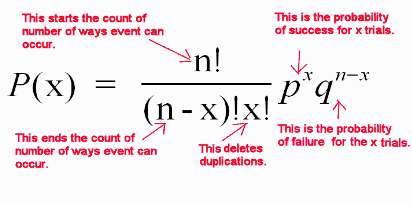
- The number of successes in the n trials is the variable.
- The probability of x successes in n independent trials is given by the formula:
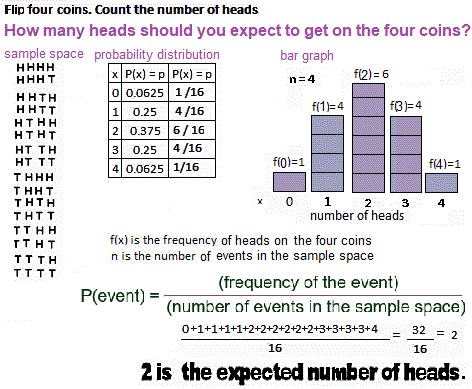
- The mean and standard deviation of a binomial distribution are stated below.

|










