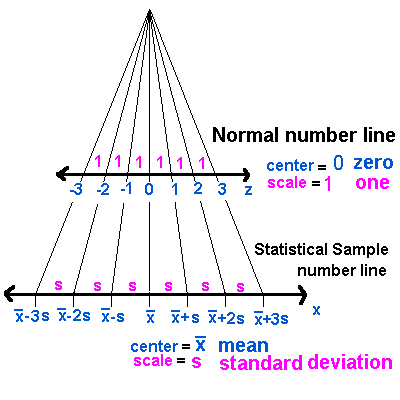
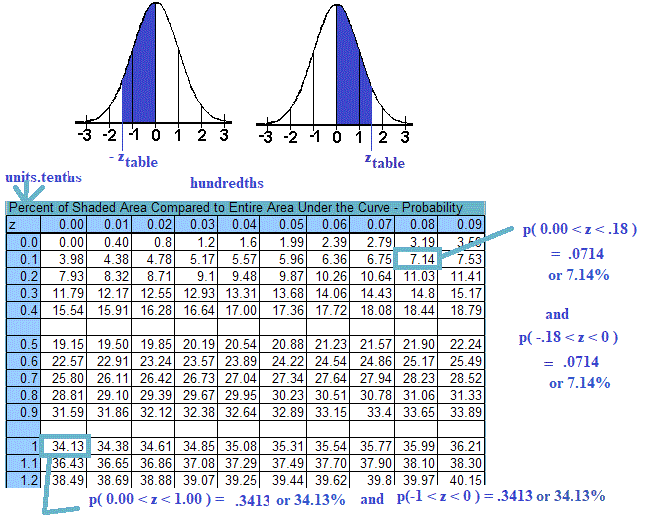
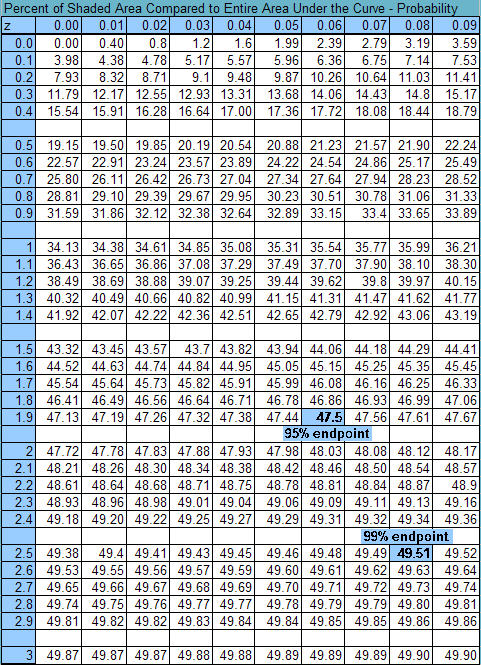
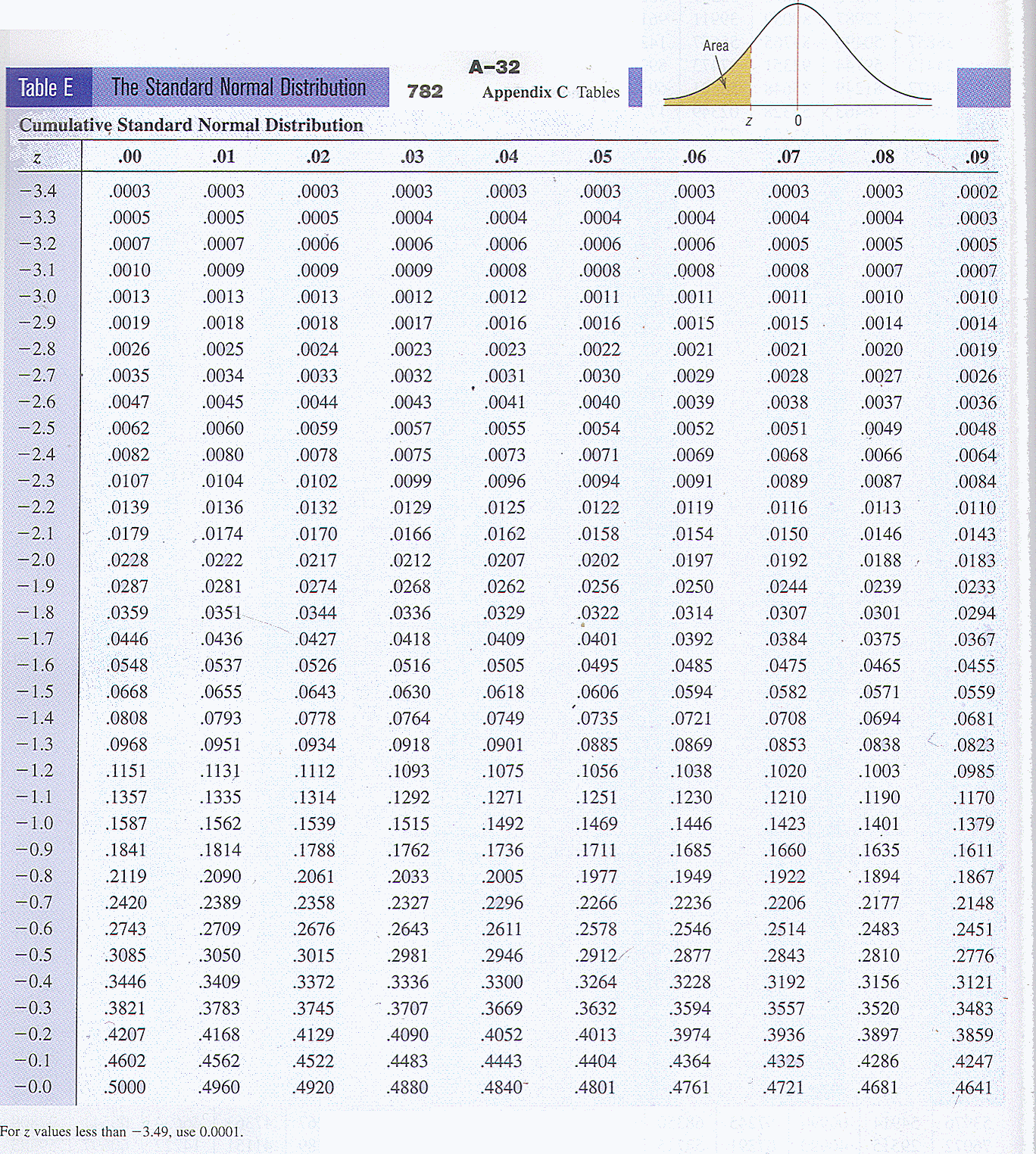
- STANDARD NORMAL TABLE OF PERCENTS/PROBABILITIES - uses z-scores and their probabilities. (above center)
- CUMULATIVE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - uses z-scores and their probabilities beginning with
z=-3 and ending with z= 3, but, lists the sum of the probabilities from
z = -3 to the desired z-score. (above right)
-
stat123sp25.A.xls - basic 1-variable & 2-variable statistics, scatterplot, regression
stat.xls -- spread sheet from the video
Area Under Curve Spread Sheet Commands Summary
- use NORMSDIST(z)
- Returns the standard normal cumulative distribution (has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one).
- use NORMSINV(probability)
- Returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution (has a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one).
- use PROB(x_range,prob_range,lower_limit.Upper_limit)
- Returns the probability that values in a range are between two limits or equal to a lower limit.
-
- Area Under the Curve
- The Probability a Score is Below a Score, Above a Score, or Between Two Scores
- The area below a score is p(x < a) and is computed with:
- =NORMDIST(a,mean,standard deviation,true)
- The area above a score is p(x > a) and is computed with:
- =1-NORMDIST(a,mean,standard deviation,true)or
- =NORMDIST(a,mean, standard deviation,false)
- The area between two score is p(b < x < a) and is computed with:
- =NORMDIST(a,mean, standard deviation,true) -
- NORMDIST(b,mean,standard deviation,true)
-
sheet 6b of ReimannSums.gsp
-- cummulative probability distribution w/32 Reimann boxes and input a and b,
from page
Mon, 2/3, in text book 2.5, 2.6, 2.7, "Center & Spread"
-
 TI83-84 STATISTICS and DISTRIBUTION Menu
TI83-84 STATISTICS and DISTRIBUTION Menu
TI DISTRIBUTION PAGE - 1:normalpdf(x[,mean,standard deviation])
- normal probability density function
- 2:normalcdf(lower bound,upper bound[,mean, standard deviation])
- normal cumulative distribution function (area under the curve)
- 3:invNorm(area[,mean,standard deviation])
- normal distribution s x-value or z-score corresponding to a known area
-
 omnicalculator.com/statistics/normal-distribution
notes
omnicalculator.com/statistics/normal-distribution
notes
|