Discrete or Continuous
- CONTINUOUS - all numbers are used over the desired interval
You might have data that are
real numbers on a range 0 < x < 6: numbers like 4.387, .58, 5.55555... or you might have real numbers from -3 to 5.
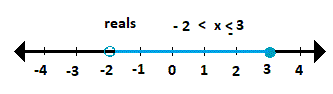 Examples:
Examples: -
- · a length of time, as in how many months till a birthday
- · a height,
- · a weight
- · the temperatures on Wednesday mornings in January
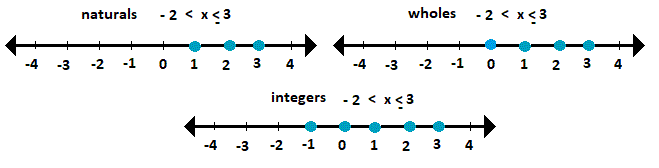
- DISCRETE - only certain numbers are used over the desired interval
You might have data that are
integers: numbers like -3, 0, -10, 4, 6, 10, 11, or
natural (counting) numbers: numbers like 1, 2, 3, 4, ...
 Examples:
Examples:
-
-
- · a shoe size, as in 8, 8 1/2, 9, 9 1/2
- · a grade in school, as in: 1st, 2nd, 3rd
-
|









