Normal and Standard Normal Distributions
- e - a constant approximately equal to 2.718281828454590, as defined below.
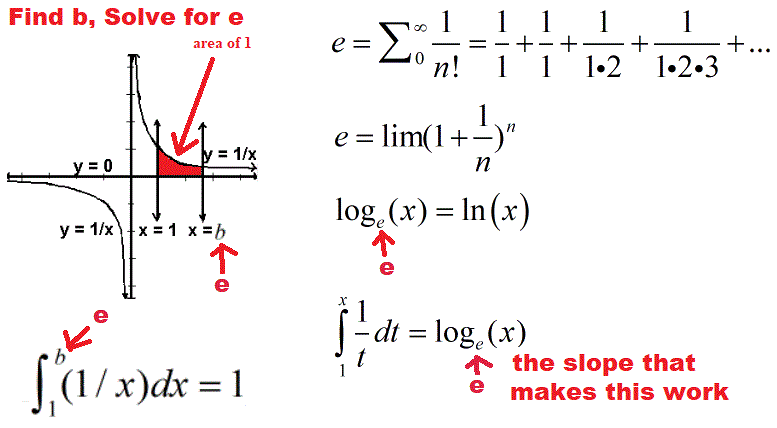
- z - the variable used to indicate workis with the standard normal distribution having a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1.
-
PI -
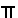 - the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, about 3.14159 or 22/7. - the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, about 3.14159 or 22/7.
- NORMAL DISTRIBUTIONS - or Gaussian distribution, a continuous probability distribution (so the area under the curve equals 1),
where the mean, mode, median are all the same, so the data gathers about a center making a symmetric bell-shaped curve.
Many data points -- heights of people, lengths of fish, errors measurements, standardized test scores have normal distributions.
- STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - a normal distribution having a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. It is very useful in computing, and looking up, probabilities, comparing samples and populations, and analysis and hypothesis testing.

- STANDARD NORMAL TABLE OF PERCENTS/PROBABILITIES - uses z-scores and their probabilities.

- CUMULATIVE STANDARD NORMAL DISTRIBUTION - uses z-scores and their probabilities beginning with z=-3 and ending with z= 3 but, lists the sum of the probabilities from z = -3 to the desired z-score.

- BELL-SHAPED CURVE - a normal distribution. It looks like a symmetric bell sitting on a table. The scores are piled in the center and trail off at the upper and lower range of variables.

- WITHIN A SPECIFIC STANDARD DEVIATION OF THE MEAN - a range of scores centered about the mean and, in either direction, not farther on the number line than the specified number of standard deviations.
ex. on the standard normal number line, "within 1 standard deviation of the mean" means, from -1 to 1, - 1 < z < 1, and includes about 68% of the scores
ex. on the normal number line, "within 3 standard deviation of the mean" means, from -3 to 3, - 3 < x < 3, and includes about 99.7% of the scores.

- CHEBYCHEV'S RULES -- for any distribution, the percent of scores within k standard deviations of the mean, k > 0, is 1/k2

|








 - a math symbol meaning "add up the terms."
- a math symbol meaning "add up the terms."
 , read as "x bar" - arithmetic average. Formula:
, read as "x bar" - arithmetic average. Formula: 
 , read as "x hat" --median, Q2, the 50th percentile, the middle data point when the data is ordered
from lowest to highest
, read as "x hat" --median, Q2, the 50th percentile, the middle data point when the data is ordered
from lowest to highest






 , the arithmetic average, the sum of the numbers divided by the number of numbers.
, the arithmetic average, the sum of the numbers divided by the number of numbers.




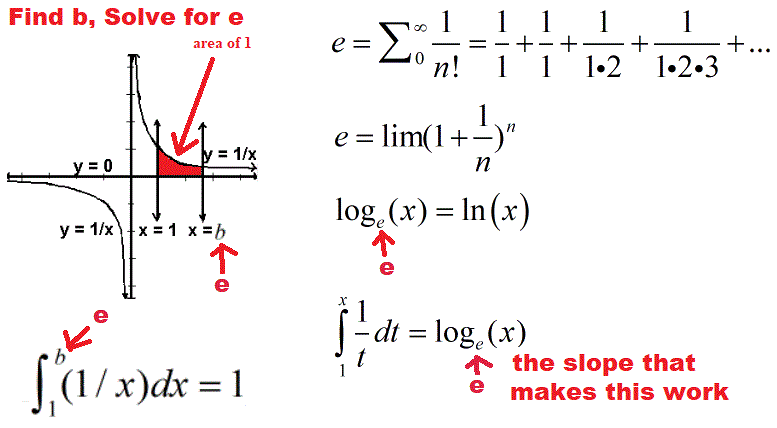
 - the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, about 3.14159 or 22/7.
- the ratio of the circumference of a circle to its diameter, about 3.14159 or 22/7.








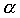 - "(1- degree of confidence)," the probability a score does not fall into the confidence interval
- "(1- degree of confidence)," the probability a score does not fall into the confidence interval 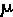 - E <
- E <

 k, where k is the null hypothesis mean.
k, where k is the null hypothesis mean.


![[MC,i. Home]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/mcihome.gif)
![[Table]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/table.gif)
![[Words]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/words.gif)
![[this semester's schedule w/links]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/gif/semestr.gif)
![[Good Stuff -- free & valuable resources]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/gif/goods.gif)