-
A Standard Normal Distribution
With Nine Specific Intervals
-
- There exists a normal distribution with a mean
of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. It is called the standard normal distribution.

-
- When the center interval is within a quarter of a standard
deviation of the mean, and each of the other intervals are a half standard deviation wide (exclusive of
the tails), the distribution has been marked in stanines -- the standard nine intervals.
It is often used to: - compare two or more distributions of data, particularly test scores.
- estimate or to compute probabilities of events involving normal distributions,
- facilitate using words rather than numbers in presenting statistical data.
- [Click on graphic to go to a printable copy.]

- The standard normal distribution and scale may be thought of
as a tool to scale up or down another normal distribution.
-
- The standard normal distribution is a tool to
translate a normal distribution into numbers which may be used to learn more information about the set of
data than was originally known.
-
- The stanine interevals are a tool to put descriptive words in
place of numbers and also to create enough intervals so that conversation about and comparison of two
or more sets of scores is meaningful.
-
- It is still a standard normal distribution, so the
same notations and variables hold: a standard normal scores (z),
the normal distribution mean (either
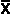 or µ), the normal distribution standard deviation, (either s or or µ), the normal distribution standard deviation, (either s or
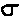 ), and the normal distribution scores (x), are used and ), and the normal distribution scores (x), are used and
-
 and and
 . .
-
- The difference is now words and less accuracy are used. For example:
-
- "Terry tested considerably above average."
-
- That means his/her score was in the 7th stanine.
|

![[next]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/next.gif)
![[last]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/last.gif)
![[next]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/next.gif)
![[last]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/last.gif)

![[MC,i. Home]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/mcihome.gif)
![[Table]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/table.gif)
![[Words]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/words.gif)

![[this semester's schedule w/links]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/gif/semestr.gif)
![[Good Stuff -- free & valuable resources]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/gif/goods.gif)
![[next]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/next.gif)
![[last]](http://www.mathnstuff.com/math/spoken/here/1gif/last.gif)